 Arbitrum One
Arbitrum One
Badges
About
Arbitrum One is a general-purpose Optimistic Rollup built by Offchain Labs and governed by the Arbitrum DAO.
Badges
About
Arbitrum One is a general-purpose Optimistic Rollup built by Offchain Labs and governed by the Arbitrum DAO.
The section shows the operating costs that L2s pay to Ethereum.
Funds can be stolen if
Funds can be lost if
MEV can be extracted if
Sequencer failure
Self sequenceState validation
Fraud proofs (INT)Fraud proofs allow actors watching the chain to prove that the state is incorrect. Interactive proofs (INT) require multiple transactions over time to resolve.
Exit window
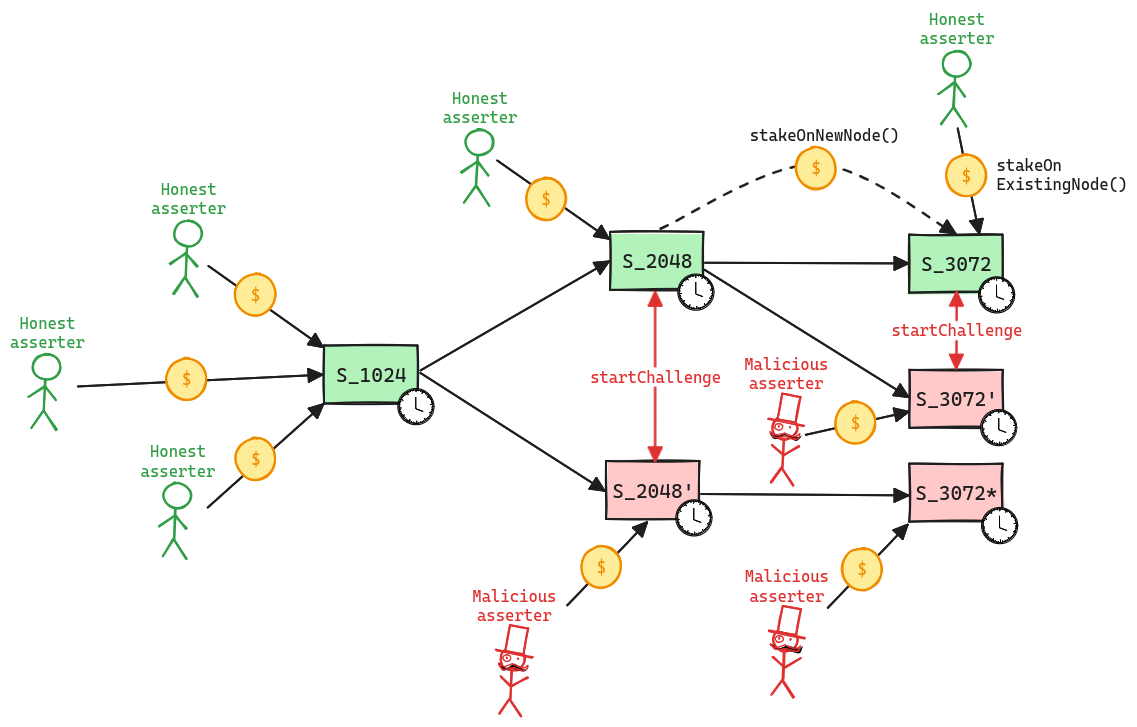
7dNon-emergency upgrades are initiated on L2 and go through a 8d delay. Since there is a 1d delay to force a tx (forcing the inclusion in the following state update), users have only 7d to exit.
If users post a tx after that time, they would only be able to self propose a state root 12d 17h after the last state root was proposed and then wait for the 6d 8h challenge window, while the upgrade would be confirmed just after the 6d 8h challenge window and the 3d L1 timelock.
Proposer failure
Self proposeAnyone can become a Proposer after 12d 17h of inactivity from the currently whitelisted Proposers.
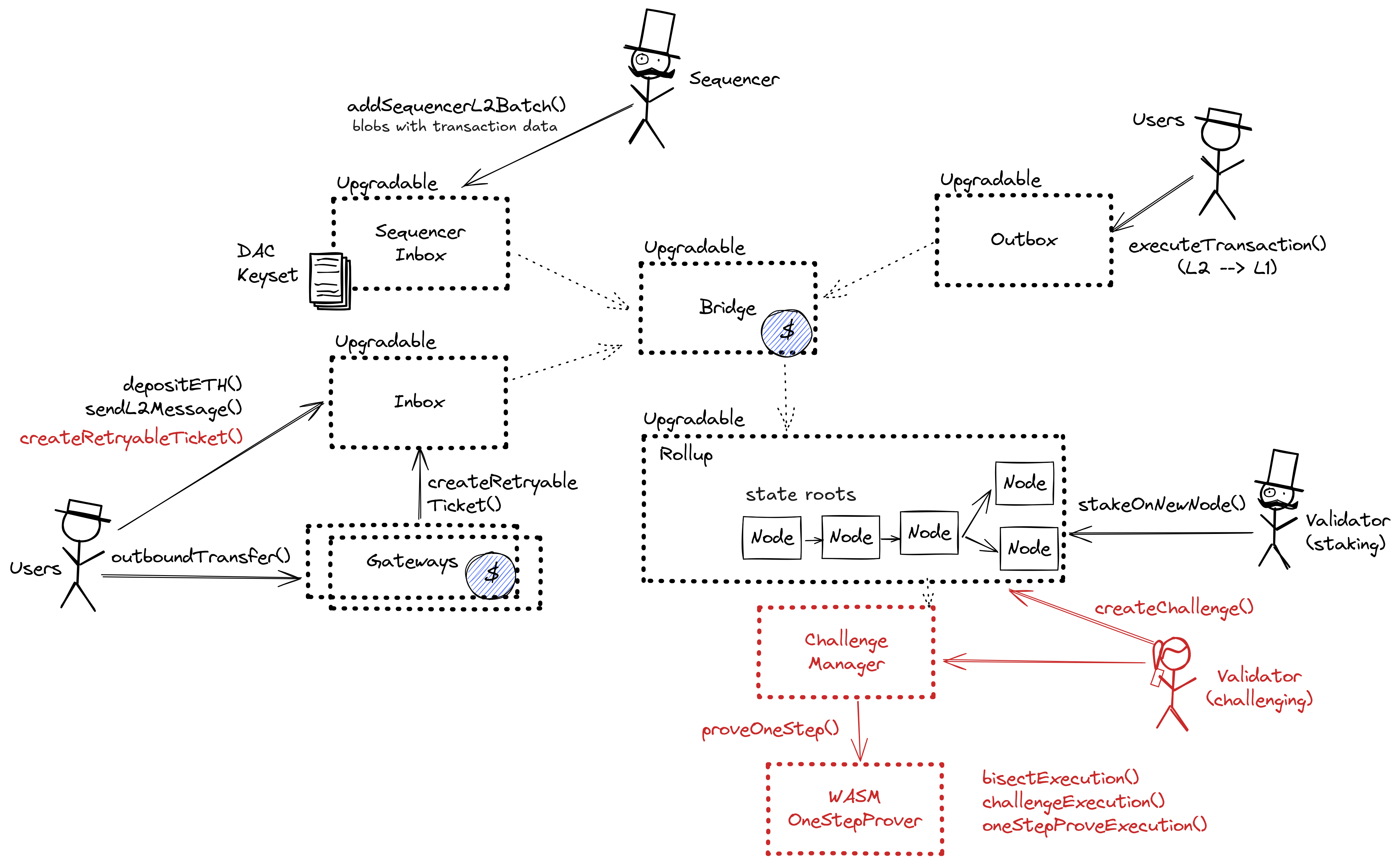
All data required for proofs is published on chain
All the data that is used to construct the system state is published on chain in the form of cheap blobs or calldata. This ensures that it will be available for enough time.
- Sequencing followed by deterministic execution - Arbitrum documentation
- SequencerInbox.sol - source code, addSequencerL2BatchFromOrigin function
The rollup node (Arbitrum Nitro) consists of four parts. The base layer is the core Geth server (with minor modifications to add hooks) that emulates the execution of EVM contracts and maintains Ethereum’s state and a fork of wasmer that is used for native WASM execution. The middle layer, ArbOS, provides additional Layer 2 functionalities such as decompressing data batches, accounting for Layer 1 gas costs, and supporting cross-chain bridge functionalities. The top layer consists of node software, primarily from Geth, that handles client connections (i.e., regular RPC node). View Code
They performed a regenesis from Classic to Nitro, and that file represents the last Classic state. To sync from the initial Classic state, instructions can be found here.
Nitro supports Ethereum’s data structures and formats by incorporating the core code of the popular go-ethereum (“Geth”) Ethereum node software. The batch is composed of a header and a compressed blob, which results from compressing concatenated RLP-encoded transactions using the standard RLP encoding.
The information in the section might be incomplete or outdated.
The L2BEAT Team is working to research & validate the content before publishing.
.
The system has a centralized sequencer
While forcing transaction is open to anyone the system employs a privileged sequencer that has priority for submitting transaction batches and ordering transactions.
MEV can be extracted if the operator exploits their centralized position and frontruns user transactions.
Users can force any transaction
Because the state of the system is based on transactions submitted on the underlying host chain and anyone can submit their transactions there it allows the users to circumvent censorship by interacting with the smart contract on the host chain directly. After a delay of 1d in which a Sequencer has failed to include a transaction that was directly posted to the smart contract, it can be forcefully included by anyone on the host chain, which finalizes its ordering.
Regular messaging
Autonomous exit
Users can (eventually) exit the system by pushing the transaction on L1 and providing the corresponding state root. The only way to prevent such withdrawal is via an upgrade.
EVM compatible and Stylus smart contracts are supported
Arbitrum One supports smart contracts written in Solidity and other programming languages (Rust, C++) that compile to WASM. Such smart contracts are executed by nodes using either a geth fork or a fork of wasmer inside the Nitro node, and can be proven with the onchain WASM VM.
Funds can be lost if there are mistakes in the highly complex Nitro and WASM one-step prover implementation.
Arbitrum DAO is in charge of upgrades
Arbitrum DAO allows $ARB token holders to propose and vote on changes to the organization and the technologies it governs. The governance smart contracts are implemented on Arbitrum One rollup chain. The DAO can upgrade the Arbitrum One contracts on L2 with 8d delay and - using L2 --> L1 Governance Relay, update contracts on L1 with additional 3d delay + 6d 8h delay for all L2 --> L1 messages (in total a delay of 17d 8h). The Security Council can upgrade the contracts without any delay. It can also cancel any upgrades initiated by the DAO.
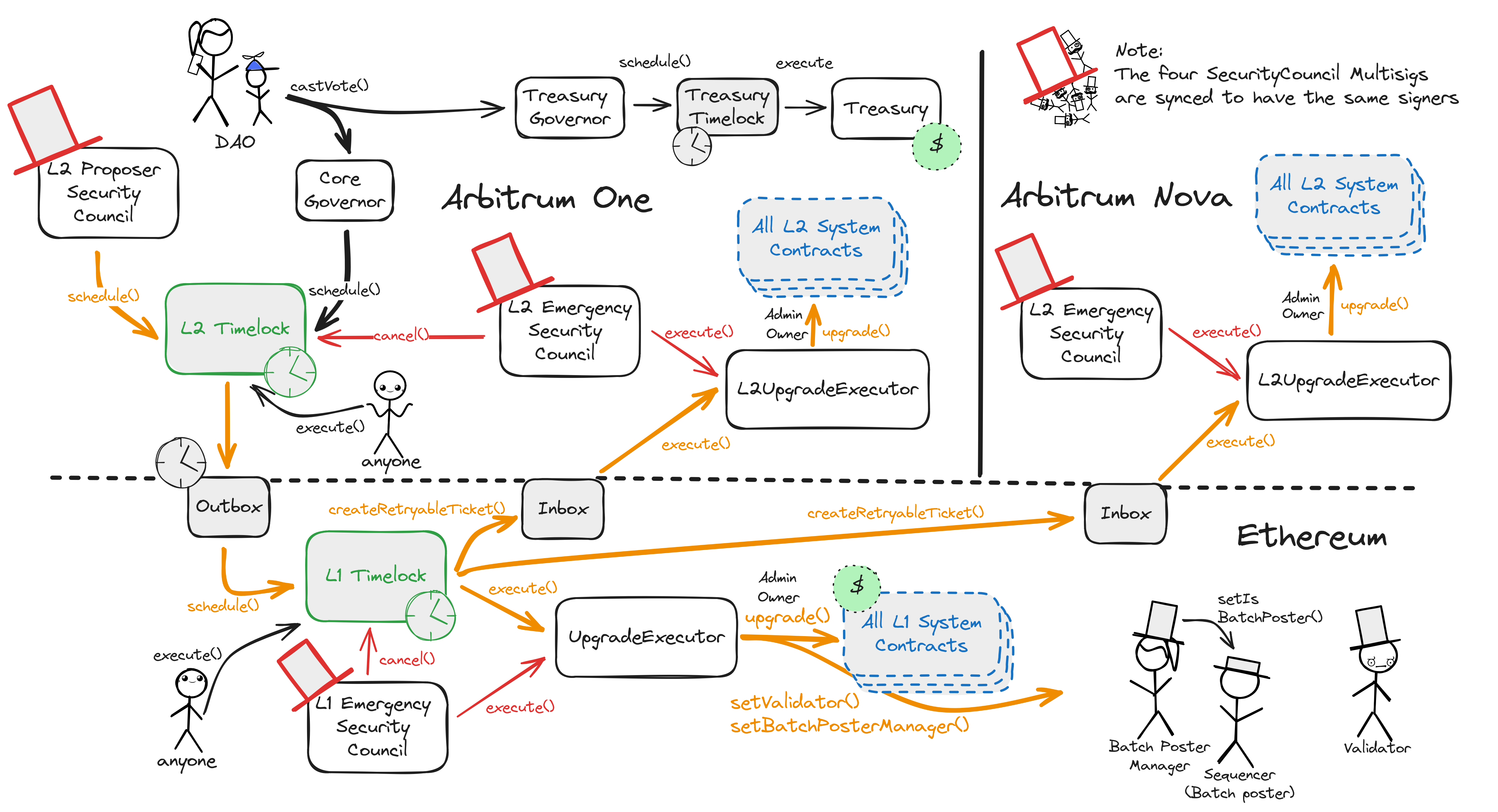
All critical system smart contracts are upgradeable (can be arbitrarily changed). This permission is governed by the Arbitrum Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) and their elected Security Council. The Arbitrum DAO controls Arbitrum One and Arbitrum Nova through upgrades and modifications to their smart contracts on Layer 1 Ethereum and the Layer 2s. While the DAO governs through token-weighted governance in their associated ARB token, the Security Council can directly act through the Security Council smart contracts on all three chains. Although these multisigs are technically separate and connect to different target permissions, their member- and threshold configuration is kept in sync by a manager contract on Arbitrum One and crosschain transactions.
Regular upgrades, Admin- and Owner actions originate from either the Arbitrum DAO or the non-emergency (proposer-) Security Council on Arbitrum One and pass through multiple delays and timelocks before being executed at their destination. Contrarily, the three Emergency Security Council multisigs (one on each chain: Arbitrum One, Ethereum, Arbitrum Nova) can skip delays and directly access all admin- and upgrade functions of all smart contracts. These two general paths have the same destination: the respective UpgradeExecutor smart contract.
Regular upgrades are scheduled in the L2 Timelock. The proposer Security Council can do this directly and the Arbitrum DAO (ARB token holders and delegates) must meet a CoreGovernor-enforced 5% threshold of the votable tokens. The L2 Timelock queues the transaction for a 8d delay and then sends it to the Outbox contract on Ethereum. This incurs another delay (the challenge period) of 6d 8h. When that has passed, the L1 Timelock delays for additional 3d. Both timelocks serve as delays during which the transparent transaction contents can be audited, and even cancelled by the Emergency Security Council. Finally, the transaction can be executed, calling Admin- or Owner functions of the respective destination smart contracts through the UpgradeExecutor on Ethereum. If the predefined transaction destination is Arbitrum One or -Nova, this last call is executed on L2 through the canonical bridge and the aliased address of the L1 Timelock.
Operator roles like the Sequencers and Validators are managed using the same paths. Sequencer changes can be delegated to a Batch Poster Manager.
Transactions targeting the Arbitrum DAO Treasury can be scheduled in the 3d Treasury Timelock by meeting a TreasuryGovernor-enforced 3% threshold of votable ARB tokens. The Security Council cannot regularly cancel these transactions or schedule different ones but can overwrite them anyway by having full admin upgrade permissions for all the underlying smart contracts.
Ethereum
Roles:
Can submit transaction batches or commitments to the SequencerInbox contract on the host chain.
Can propose new state roots (called nodes) and challenge state roots on the host chain.
Actors:
A Validator - Can propose new state roots (called nodes) and challenge state roots on the host chain.
A Validator - Can propose new state roots (called nodes) and challenge state roots on the host chain.
A Validator - Can propose new state roots (called nodes) and challenge state roots on the host chain.
- Contract used to relay governance action messages from Arbitrum One to Ethereum. It is also an escrow contract for the project’s gas token (can be different from ETH). Keeps a list of allowed Inboxes and Outboxes for canonical bridge messaging.
- Can act on behalf of L1Timelock with 3d delay.
- Is allowed to interact with RollupProxy - Pause and unpause and set important roles and parameters in the system contracts: Can delegate Sequencer management to a BatchPosterManager address, manage data availability and DACs, set the Sequencer-only window, introduce an allowList to the bridge and whitelist Inboxes/Outboxes - acting via UpgradeExecutor, L1Timelock with 3d delay.
- Is allowed to interact with L1Timelock - cancel queued transactions - acting via UpgradeExecutor, L1Timelock with 3d delay.
- Is allowed to interact with L1Timelock - propose transactions.
- Is allowed to interact with L1Timelock - update the minimum delay of the timelock - acting via UpgradeExecutor, L1Timelock with 3d delay.
- Can upgrade the implementation of Outbox, SequencerInbox, Inbox, RollupEventInbox, OutboxV0, OutboxV1, Bridge, ChallengeManager - acting via ArbitrumProxyAdmin, UpgradeExecutor, L1Timelock with 3d delay.
- Can upgrade the implementation of UpgradeExecutor, L1Timelock - acting via UpgradeExecutorAdmin, UpgradeExecutor, L1Timelock with 3d delay.
- Can upgrade the implementation of RollupProxy - acting via UpgradeExecutor, L1Timelock with 3d delay.
- Can upgrade the implementation of L1GatewayRouter, L1ERC20Gateway, L1CustomGateway - acting via GatewaysAdmin, UpgradeExecutor, L1Timelock with 3d delay.
Used in:
A Validator - Can propose new state roots (called nodes) and challenge state roots on the host chain.
A Validator - Can propose new state roots (called nodes) and challenge state roots on the host chain.
- A Multisig with 4 / 6 threshold.
- Can act on behalf of ProxyAdmin, ProxyAdmin.
- Can upgrade the implementation of ValidatorWallet, ValidatorWallet - acting via ProxyAdmin.
Used in:
- A Multisig with 4 / 6 threshold.
- Is allowed to interact with SequencerInbox - Add/remove batchPosters (Sequencers).
Used in:
- A Multisig with 9 / 12 threshold. It uses the following modules: UpgradeExecutor (Central contract defining the access control permissions for upgrading the system contract implementations).
- Can act on behalf of UpgradeExecutor.
- Is allowed to interact with RollupProxy - Pause and unpause and set important roles and parameters in the system contracts: Can delegate Sequencer management to a BatchPosterManager address, manage data availability and DACs, set the Sequencer-only window, introduce an allowList to the bridge and whitelist Inboxes/Outboxes - acting via UpgradeExecutor.
- Is allowed to interact with L1Timelock - cancel queued transactions - acting via UpgradeExecutor.
- Is allowed to interact with L1Timelock - update the minimum delay of the timelock - acting via UpgradeExecutor.
- Can upgrade the implementation of Outbox, SequencerInbox, Inbox, RollupEventInbox, OutboxV0, OutboxV1, Bridge, ChallengeManager - acting via ArbitrumProxyAdmin, UpgradeExecutor.
- Can upgrade the implementation of UpgradeExecutor, L1Timelock - acting via UpgradeExecutorAdmin, UpgradeExecutor.
- Can upgrade the implementation of RollupProxy - acting via UpgradeExecutor.
- Can upgrade the implementation of L1GatewayRouter, L1ERC20Gateway, L1CustomGateway - acting via GatewaysAdmin, UpgradeExecutor.
Participants (12):
AleksanderKryukov-CertoraDennisonBertram-TallyJohnMorrow-GauntletGoncaloMagalhaes-Immunefigzeon-OffchainLabsEmilianoBonassi-ConduitGriffGreen-GivethStevenThornton-OpenZeppelincts-Zellicfred-Arbitrumbartek.eth-L2BEATyoav.eth-EFUsed in:
A Validator - Can propose new state roots (called nodes) and challenge state roots on the host chain.
Can upgrade the implementation of FundRetriever.
Can upgrade the implementation of ValidatorWallet - acting via ProxyAdmin.
Can upgrade the implementation of ValidatorWallet - acting via ProxyAdmin.
Can upgrade the implementation of ValidatorWallet - acting via ProxyAdmin.
Can upgrade the implementation of Validator - acting via ProxyAdmin.
Arbitrum One
Actors:
- A Multisig with 9 / 12 threshold. It uses the following modules: L2UpgradeExecutor (This contract can upgrade the L2 system’s contracts through the L2ProxyAdmin. The upgrades can be done either by the Security Council or by the L1Timelock (via its alias on L2)).
- Can act on behalf of L2UpgradeExecutor.
- Is allowed to interact with L2Timelock - update the minimum delay of the timelock - acting via L2UpgradeExecutor.
- Can upgrade the implementation of L2ERC20Gateway, L2GatewayRouter, L2WethGateway - acting via L2GatewaysProxyAdmin, L2UpgradeExecutor.
- A Multisig with 9 / 12 threshold. It uses the following modules: L2UpgradeExecutor (This contract can upgrade the L2 system’s contracts through the L2ProxyAdmin. The upgrades can be done either by the Security Council or by the L1Timelock (via its alias on L2)).
- Can act on behalf of L2Timelock with 8d delay.
- Is allowed to interact with L2Timelock - propose transactions.
- This contract enforces the rules for changing members and cohorts of the SecurityCouncil and creates crosschain messages to Ethereum and Arbitrum Nova to keep the configuration in sync.
- Can act on behalf of L2Timelock with 8d delay.
- Is allowed to interact with L2Timelock - propose transactions.
- The owner (UpgradeExecutor) can upgrade proxies’ implementations of all L2 system contracts through this contract.
- Can upgrade the implementation of L2Timelock, TreasuryGovernor, L2ArbitrumToken, TreasuryTimelock, L2ARBGateway, L2UpgradeExecutor, SecurityCouncilManager, CoreGovernor.
- Governance contract accepting and managing constitutional Arbitrum Improvement Proposals (AIPs, core proposals) and, among other formal parameters, enforcing the 5% quorum for proposals.
- Can act on behalf of L2Timelock with 8d delay.
- Is allowed to interact with L2Timelock - cancel queued transactions.
- Is allowed to interact with L2Timelock - propose transactions.
A Multisig with 1 / 13 threshold.
Participants (13):
0x526C…49EF0xf8e1…fEfd0x0E50…eBf50x8688…96230x8891…a2170x8e62…a3C50x566a…37100x5280…2e44bartek.eth-L2BEAT0x5A1F…81dF0xf6B6…C863yoav.eth-EF0x5772…FEECUsed in:
- Is allowed to interact with L2Timelock - update the minimum delay of the timelock - acting via L2UpgradeExecutor.
- Can upgrade the implementation of L2ERC20Gateway, L2GatewayRouter, L2WethGateway - acting via L2GatewaysProxyAdmin, L2UpgradeExecutor.
Ethereum
Can be used to upgrade implementation of ValidatorWallet.
This contract stores the following tokens: wstETH.
One of the modular contracts used for the last step of a fraud proof, which is simulated inside a WASM virtual machine.
Implementation used in:
Can be used to upgrade implementation of ValidatorWallet.
Can be used to upgrade implementation of ValidatorWallet.
Can be used to upgrade implementation of ValidatorWallet.
Can be used to upgrade implementation of Outbox, SequencerInbox, Inbox, RollupEventInbox, OutboxV0, OutboxV1, Bridge, ChallengeManager.
Implementation used in:
Can be used to upgrade implementation of UpgradeExecutor, L1Timelock.
Implementation used in:
One of the modular contracts used for the last step of a fraud proof, which is simulated inside a WASM virtual machine.
Implementation used in:
Central contract for the project’s configuration like its execution logic hash (wasmModuleRoot) and addresses of the other system contracts. Entry point for Proposers creating new Rollup Nodes (state commitments) and Challengers submitting fraud proofs (In the Orbit stack, these two roles are both held by the Validators).
Implementation used in:
This contract stores the following tokens: LPT.
This routing contract maps tokens to the correct escrow (gateway) to be then bridged with canonical messaging.
Implementation used in:
One of the modular contracts used for the last step of a fraud proof, which is simulated inside a WASM virtual machine.
Implementation used in:
Can be used to upgrade implementation of L1GatewayRouter, L1ERC20Gateway, L1CustomGateway.
This contract implements view only utilities for validators.
This contract stores the following tokens: DAI.
One of the modular contracts used for the last step of a fraud proof, which is simulated inside a WASM virtual machine.
Implementation used in:
Escrows deposited ERC-20 assets for the canonical Bridge. Upon depositing, a generic token representation will be minted at the destination. Withdrawals are initiated by the Outbox contract. This contract can store any token.
Implementation used in:
Can be used to upgrade implementation of Validator.
Can be used to upgrade implementation of ValidatorWallet.
Escrows deposited assets for the canonical bridge that are externally governed or need custom token contracts with e.g. minting rights or upgradeability. This contract can store any token.
Implementation used in:
One of the modular contracts used for the last step of a fraud proof, which is simulated inside a WASM virtual machine.
Implementation used in:
Contract that allows challenging state roots. Can be called through the RollupProxy by Validators or the UpgradeExecutor.
Implementation used in:
- A timelock with access control. The current minimum delay is 3d. Proposals that passed their minimum delay can be executed by the anyone.
- Can act on behalf of UpgradeExecutor.
Proxy used in:
A sequencer (registered in this contract) can submit transaction batches or commitments here.
Implementation used in:
Helper contract sending configuration data over the bridge during the systems initialization.
Arbitrum One
Keeps the current hash of the ArbitrumDAO Constitution. Settable by the L2UpgradeExecutor.
This contract receives all SurplusFees: Transaction fee component that covers the cost beyond that covered by the L2 Base Fee during chain congestion. They are withdrawable to a configurable set of recipients.
Delays constitutional AIPs from the CoreGovernor by 8d.
Counterpart to the L1DaiGateway. Can mint (deposit to L2) and burn (withdraw to L1) DAI tokens on L2.
Implementation used in:
Router managing token <–> gateway mapping on L2.
Governance contract used for creating non-constitutional AIPs, or “treasury proposals”, e.g., transferring founds out of the DAO Treasury. Also enforces the 3% quorum for proposals.
The ARB token contract. Supply can be increased by the owner once per year by a maximum of 2%.
Contract used by the security council management system to sync SecurityCouncil members between the L1 and the L2.
This contract receives all BaseFees: The transaction fee component that covers the minimum cost of Arbitrum transaction execution. They are withdrawable to a configurable set of recipients.
Delays treasury proposals from the TreasuryGovernor by 259200 seconds. Is used as the main recipient for the ETH from L2SurplusFee and L2BaseFee contracts.
Can be used to upgrade implementation of L2ERC20Gateway, L2GatewayRouter, L2WethGateway.
Value Secured is calculated based on these smart contracts and tokens:
Main entry point for users depositing ERC20 tokens that require minting custom tokens on L2.
Implementation used in:
Main entry point for users depositing ERC20 tokens. Upon depositing, on L2 a generic, “wrapped” token will be minted.
Implementation used in:
DAI Vault for custom DAI Gateway. Fully controlled by MakerDAO governance.
wstETH Vault for custom wstETH Gateway. Fully controlled by Lido governance.
LPT Vault for custom Livepeer Token Gateway.
Contract managing Inboxes and Outboxes. It escrows ETH sent to L2.
Proxy used in:
The current deployment carries some associated risks:
Funds can be stolen if a contract receives a malicious code upgrade. There is a 17d 8h delay on code upgrades unless upgrade is initiated by the Security Council in which case there is no delay.

